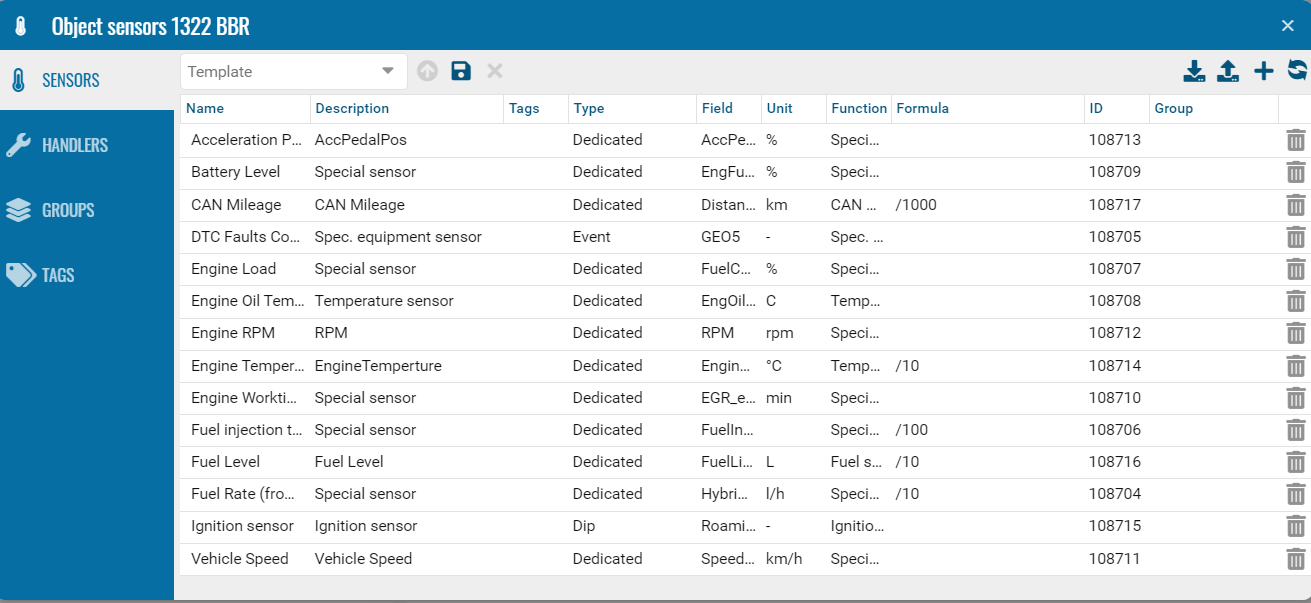
Add Sensors
The most common sensors are sensors for ignition operation, fuel level control, special equipment operation control, GSM, GPS, and on-board power supply voltage.
To create and configure sensors in the Pilot system, you need to complete the following steps:
1. In the object’s context menu, click add + sensor (see quick start).
2. Select the type of sensor you want to add, such as temperature, fuel level or door sensor.
3. Configure sensor parameters such as thresholds, update rate, and other specific settings.
4. Save your changes and check that the sensor appears in the list of active sensors and is sending data correctly.
Enter settings
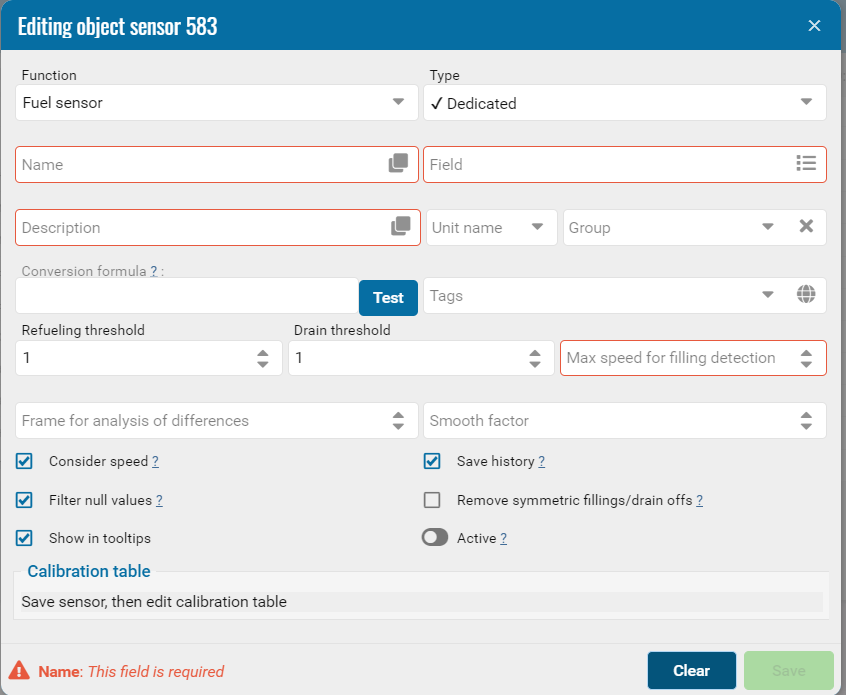
• Select the sensor purpose
• Copy the name of the same field
• Select the type
• Select a field from the list.
• Set the threshold "Minimum filling" and "Minimum drain".
• And also add other settings (save history, take speed into account, filter value).
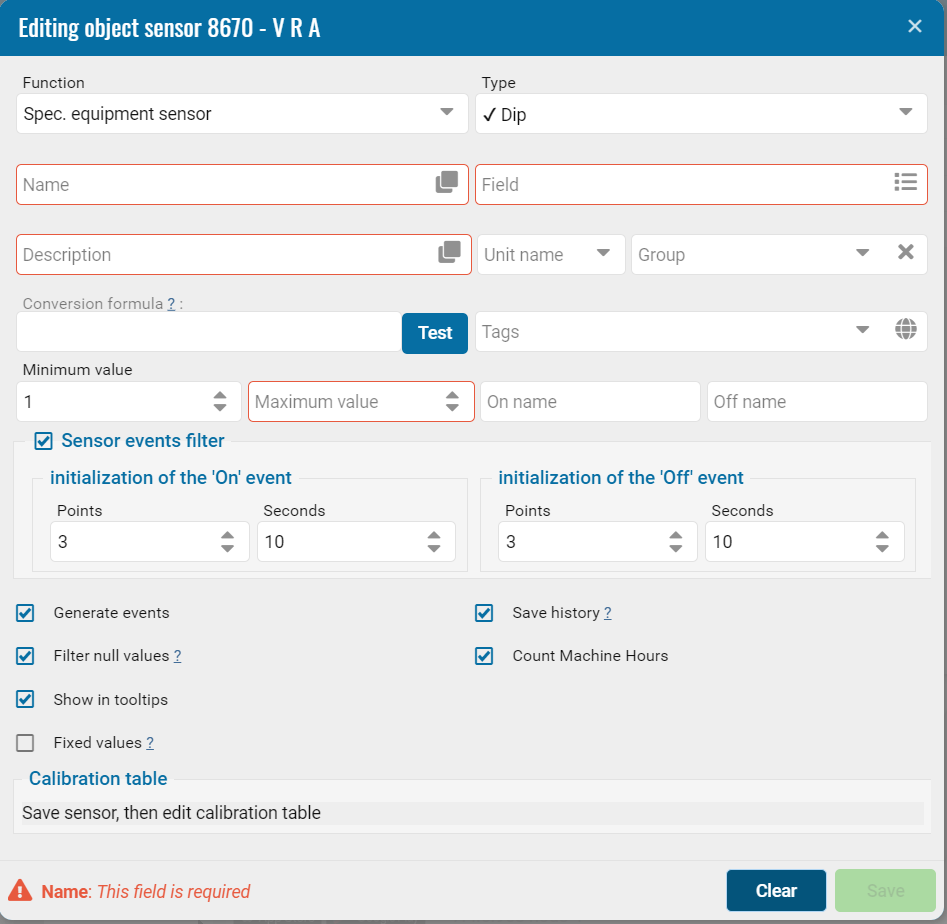
Sensor events filter
The trigger delay filter is a function in the control system that is designed to prevent false or premature triggering. This can be especially useful in systems where false alarms due to short-term interference or parameter fluctuations need to be avoided.
Trigger delay filter for "On" and "Off" events
The trigger delay filter can be configured by the number of packets received from the device or by time in seconds.
For example, if you specify a value of 3, the third packet will transmit information about whether the sensor is on or off. Similarly, you can set the interval to 10 seconds, and the system will determine whether the sensor was on or off during this time.
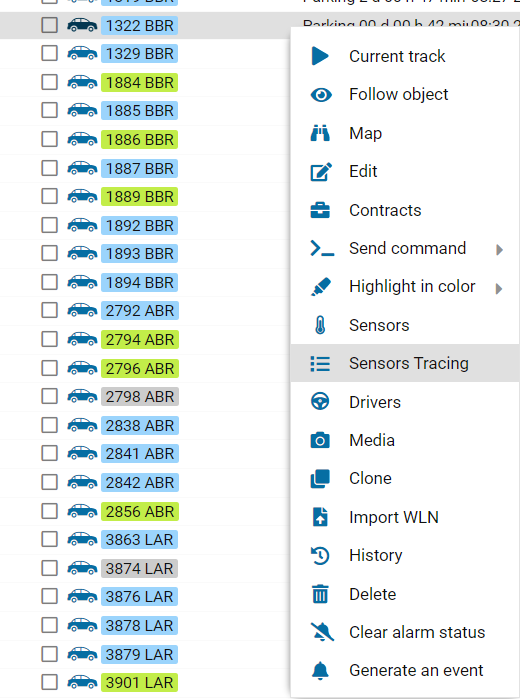
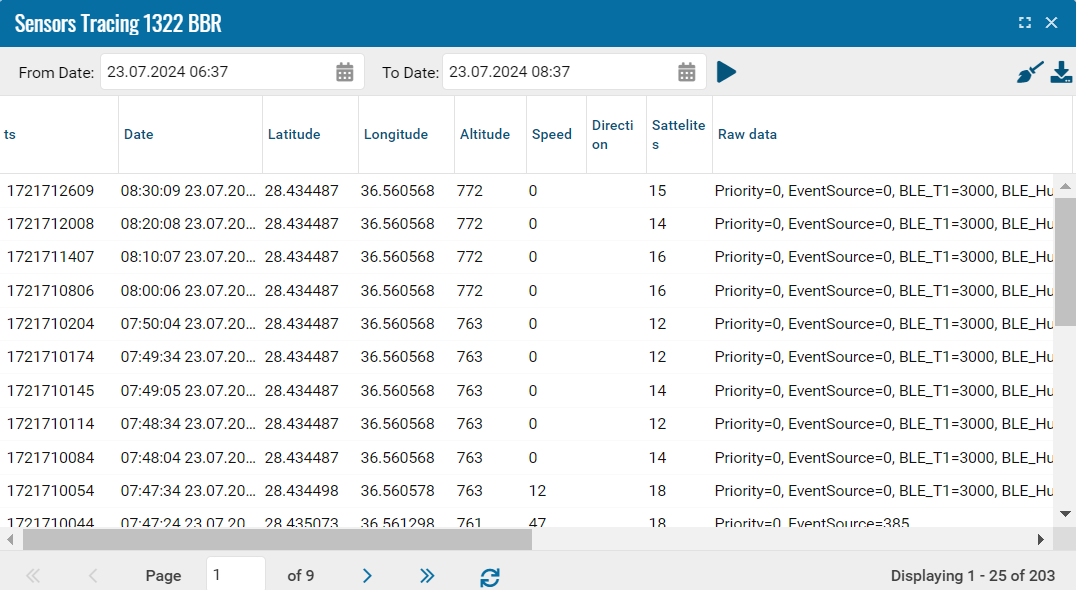
You can check the received sensor values in the Sensor Tracing section in the object’s context menu.
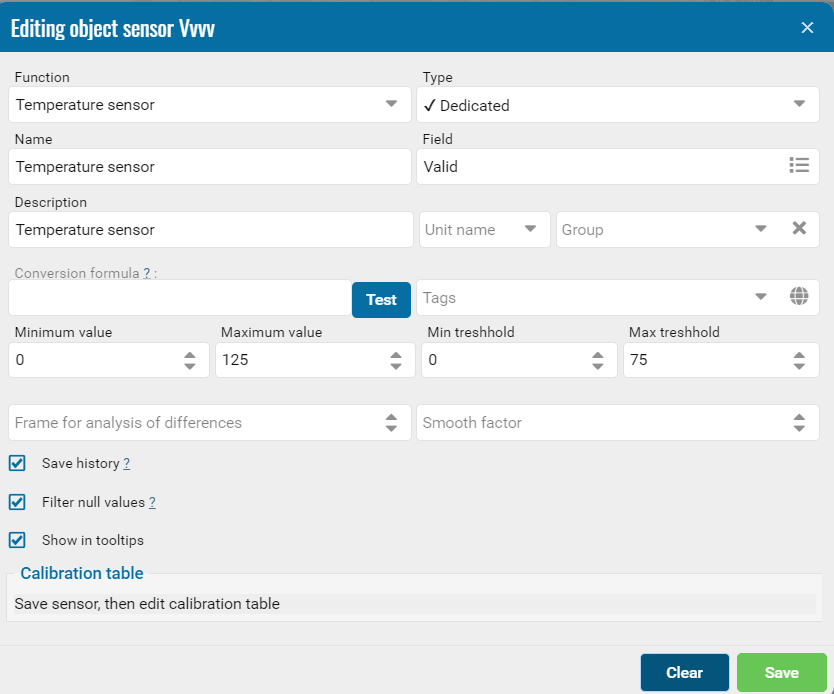
Let's look at another feature for the Temperature sensor.
Several important filters can be applied to this sensor:
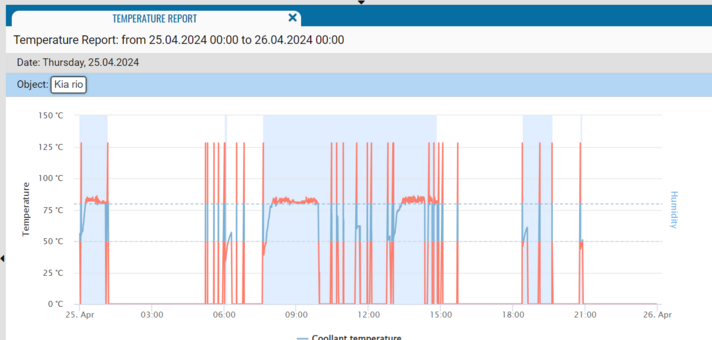
1. Min and Max treshhold. The normal temperature of the sensor, highlighted in green dotted line on the graph.
2. Min and Max (incorrect) values. In red on the graph.
Designed to not take into account invalid values or error codes.
The system will cut off such temperature values and not take them into account when generating reports.
3. Number of points for detecting threshold exceedance.
Specifies how many measurements in a row should record the threshold exceedance for the system to consider this event reliable and start responding to it.
For example, if the value is set to 6, this means that the sensor must record the threshold exceedance at least 6 times in a row before the system starts signaling the exceedance.
This setting helps to avoid false alarms due to short-term temperature fluctuations or other interference, ensuring more stable and accurate system operation.
4. The smoothing factor in the temperature sensor affects how quickly and efficiently the sensor responds to temperature changes. This value determines how much the data will be smoothed during processing. A high smoothing factor can help reduce the impact of random fluctuations.
Link to video
Add a sensor to the system:https://youtu.be/9dYchFyidIs
|